Unlocking the Power of Foundry Casting: Versatility, Innovation, and Economic Impact
Release time:
2024-04-20
Foundry Casting Definition
Foundry casting is a manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mold cavity to create solid metal objects of desired shapes and sizes. This method is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction for producing various components and parts.
Contact YAQI to manufacture the castings you desire.
why foundry casting is widely used?
Foundry casting is widely used for several reasons:
Versatility: Foundry casting can produce complex shapes and intricate parts that may be difficult or impossible to create using other manufacturing methods.
Cost-effectiveness: Foundry casting can be a cost-effective method for producing large quantities of metal parts, as the initial tooling costs can be spread out over the production run.
Material flexibility: Foundry casting can be used with a wide range of metals and alloys, allowing manufacturers to choose materials that best suit their specific application requirements.
Strength and durability: Cast metal parts typically exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and durability, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Efficiency: Foundry casting processes can be highly automated, resulting in efficient production and reduced labor costs.
Design freedom: Foundry casting allows for flexibility in design, enabling the creation of customized components tailored to specific needs or requirements.
The versatility, cost-effectiveness, material flexibility, strength, efficiency, and design freedom offered by foundry casting make it a popular choice for manufacturers across various industries.

Why Is Foundry Casting Important?
Foundry casting is important for several reasons:
-
Manufacturing Components: Foundry casting is essential for producing a wide range of metal components used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery manufacturing.
-
Versatility: It allows for the production of complex shapes and intricate parts that are difficult or impossible to create using other manufacturing methods, offering designers and engineers greater flexibility in product design.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Foundry casting can be a cost-effective method for producing large quantities of metal parts, particularly for complex shapes, as it often requires less machining and material waste compared to other manufacturing processes.
-
Material Flexibility: Foundry casting supports a wide range of metals and alloys, allowing manufacturers to choose materials with specific properties such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance to meet the requirements of diverse applications.
-
Strength and Durability: Cast metal parts typically exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength, durability, and wear resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications where reliability is crucial.
-
Sustainable Manufacturing: Foundry casting can be environmentally friendly, as it enables the recycling of scrap metal and minimizes material waste through precise mold design and optimization of casting processes.
-
Economic Impact: Foundry casting plays a significant role in driving economic growth by providing employment opportunities, supporting local industries, and contributing to the development of infrastructure and technology.
Overall, foundry casting is important because it enables the efficient production of high-quality metal components, fosters innovation in product design, supports economic development, and contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices.

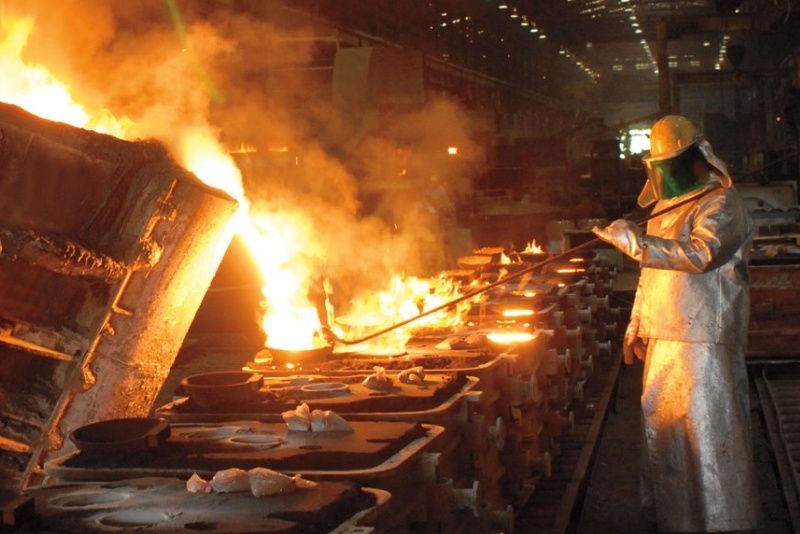
Types of Foundry Casting Metals
Foundry casting can be used with a variety of metals and alloys, depending on the specific application requirements. Some common metals and alloys used in foundry casting include:
Iron: Cast iron is one of the most widely used metals in foundry casting due to its excellent castability, high strength, and wear resistance. Common types of cast iron include gray iron, ductile iron, and malleable iron.
Steel: Steel casting is prevalent in industries where strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance are essential. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel are commonly cast using foundry processes.
Aluminum: Aluminum casting is favored for its lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. It is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries.
Copper and Copper Alloys: Copper and its alloys, such as bronze and brass, are used in foundry casting for their electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. They are often employed in architectural applications and artistic castings.
Zinc: Zinc casting is valued for its excellent casting properties, such as fluidity and low melting point, making it suitable for producing intricate and detailed parts in various industries.
Magnesium: Magnesium casting offers lightweight properties, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, and good machinability, making it ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
Nickel and Nickel Alloys: Nickel-based alloys are known for their high temperature and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications in chemical processing, aerospace, and marine industries.
Titanium: Titanium casting is used in aerospace, medical, and military applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
These are just a few examples of the metals and alloys commonly used in foundry casting. The selection of the appropriate material depends on factors such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and cost considerations for specific applications.
Summary:
Foundry casting is a pivotal manufacturing process utilized across industries for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, material flexibility, and ability to produce durable, complex components. With its significance lying in economic impact, sustainability, and innovation, foundry casting remains indispensable in modern manufacturing. The diverse range of metals and alloys compatible with this method ensures adaptability to various application requirements, further emphasizing its importance in driving industrial progress.
Key words:
Previous Page
Previous Page:
Recommended News