What is the difference between foundry and founding casting?
Release time:
2024-04-10
What does foundry mean?
A foundry is a specialized manufacturing facility where metal casting processes take place. In a foundry, metals are melted and poured into molds to produce metal parts or components of various shapes and sizes. Foundries typically handle a wide range of metals, including iron, steel, aluminum, copper, and alloys.
The primary processes in a foundry include:
Melting: Raw materials such as metal scrap, ingots, or pig iron are melted in furnaces at high temperatures to form molten metal.
Molding: Molds are created using sand, clay, or other materials to define the shape and form of the desired metal part. The mold cavity is typically formed by packing sand around a pattern (a replica of the desired part) or by using pre-made molds.
Pouring: Once the metal is molten and the mold is prepared, the molten metal is poured into the mold cavity through a pouring system, such as a sprue or gate.
Solidification: The molten metal cools and solidifies inside the mold cavity, taking the shape of the mold and forming the final casting.
Removal and Finishing: After solidification, the casting is removed from the mold and undergoes finishing processes such as trimming, cleaning, machining, and surface treatment to achieve the desired final product.
Foundries play a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, manufacturing, and more, by providing a wide range of metal components used in diverse applications.
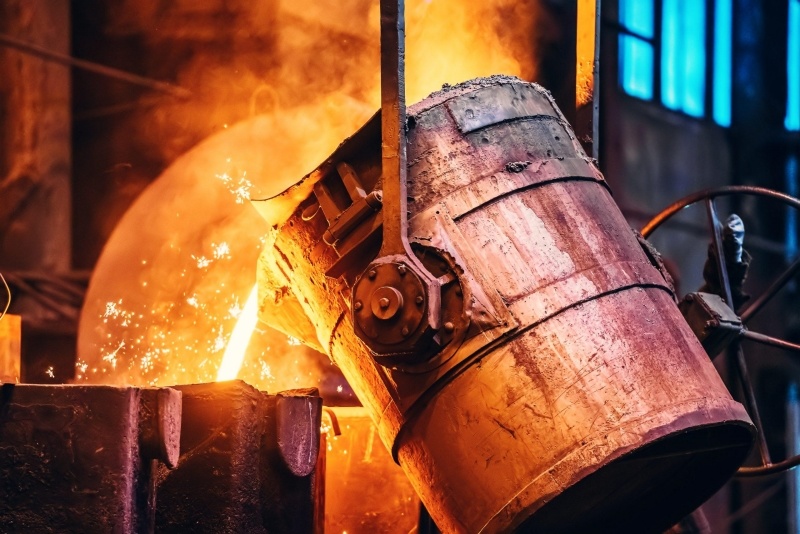

What is the difference between foundry and founding casting?
"Foundry" and "foundry casting" are closely related terms, but they refer to slightly different concepts:
Foundry: A foundry is a facility where metal casting processes take place. It is a manufacturing plant that specializes in melting metals and pouring them into molds to create metal parts or components. Foundries typically house equipment and machinery for melting, casting, molding, and finishing metal products.
Foundry Casting: Foundry casting, on the other hand, specifically refers to the process of creating metal objects by pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to solidify. This process is also known as metal casting or simply casting. Foundry casting can involve various techniques, such as sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and centrifugal casting, each with its own advantages and applications.
In sum, a foundry is the facility where metal casting processes occur, while foundry casting is the actual process of creating metal objects through casting within a foundry.
Is a steel mill the same as a foundry?
While both steel mills and foundries are involved in the production of metal products, they are distinct facilities with different functions:
Steel Mill: A steel mill, also known as a steelworks or steel plant, is an industrial facility where raw materials such as iron ore, coal, and limestone are converted into steel. The primary processes in a steel mill include melting, refining, casting, and rolling or forming the steel into various shapes and products. Steel mills typically produce large quantities of steel ingots, slabs, billets, or coils, which are then further processed by manufacturers into finished products such as beams, pipes, sheets, and bars.
Foundry: A foundry is a specialized manufacturing facility where metal casting processes take place. Foundries primarily focus on melting metals and pouring them into molds to create metal parts or components. Foundries use various casting techniques, such as sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and centrifugal casting, to produce a wide range of metal products. While some foundries may produce steel castings, they also work with other metals such as iron, aluminum, copper, and alloys.
While both steel mills and foundries are involved in metal production, steel mills primarily produce steel through melting and refining processes, while foundries specialize in casting metal parts and components using molds and casting techniques.
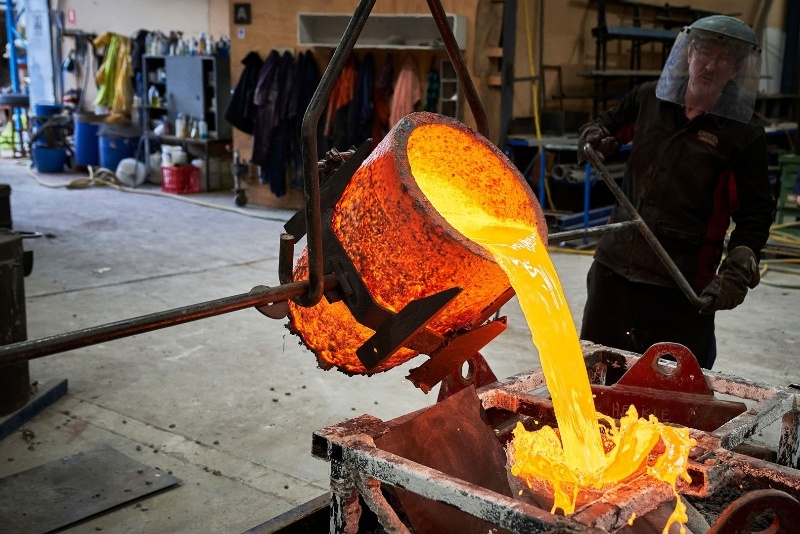

What are three main types of casting processes?
The three main types of casting processes are:
Sand Casting: Sand casting is one of the most versatile and widely used casting processes. It involves creating a mold made of sand (typically mixed with a binder to hold its shape) around a pattern of the desired part. Molten metal is then poured into the mold cavity, where it solidifies to form the final casting. Sand casting is suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals and can produce complex shapes with relatively low tooling costs.
Investment Casting: Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, is a precision casting process that is used to produce parts with high accuracy and intricate details. In this process, a wax pattern of the desired part is created and coated with a refractory material to form a ceramic shell. The wax is then melted out of the shell, leaving behind a hollow cavity. Molten metal is poured into the cavity, filling the space left by the wax pattern. Investment casting is often used for small to medium-sized parts made of various metals and alloys.
Die Casting: Die casting is a casting process that involves injecting molten metal into a steel mold cavity under high pressure. The mold, also known as a die, is typically made of two halves that are mounted on a machine. Die casting is highly efficient and produces parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finish. It is commonly used for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts, such as automotive components, consumer electronics, and household appliances. Die casting can be further categorized into hot chamber and cold chamber die casting, depending on whether the metal is melted within the machine (hot chamber) or in an external furnace (cold chamber) before injection.
All in all, foundries are specialized manufacturing facilities where metal casting processes take place, involving melting metals and pouring them into molds to create various parts and components. Foundry casting encompasses a range of techniques like sand casting, investment casting, and die casting, each suited to different applications. While similar in metal production, steel mills primarily focus on refining raw materials into steel, while foundries specialize in casting metal parts. Understanding these distinctions can help clarify the roles each facility plays in the broader manufacturing landscape.
If there is more you want to know, welcome to contact Yaqi!
Key words:
Recommended News